奥村泰之,樋口輝彦:
日本におけるうつ病の経済損失/疾病費用
http://dx.crossref.org/10.4088%2FPCC.10m01082 |
Okumura Y, Higuchi T:
Cost of depression among adults in Japan.
The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders 13(3): e1–e9, 2011. |
| うつ病が社会に与える影響は甚大であり、その経済損失は1年間 (2008年) で、1兆2900億円であると計上された。 損失のうち医療費が占める割合は14.2%であり、自殺による将来所得の損失が23.1%、欠勤や労働生産性の低下による損失が62.7%であることが明らかになった。 |
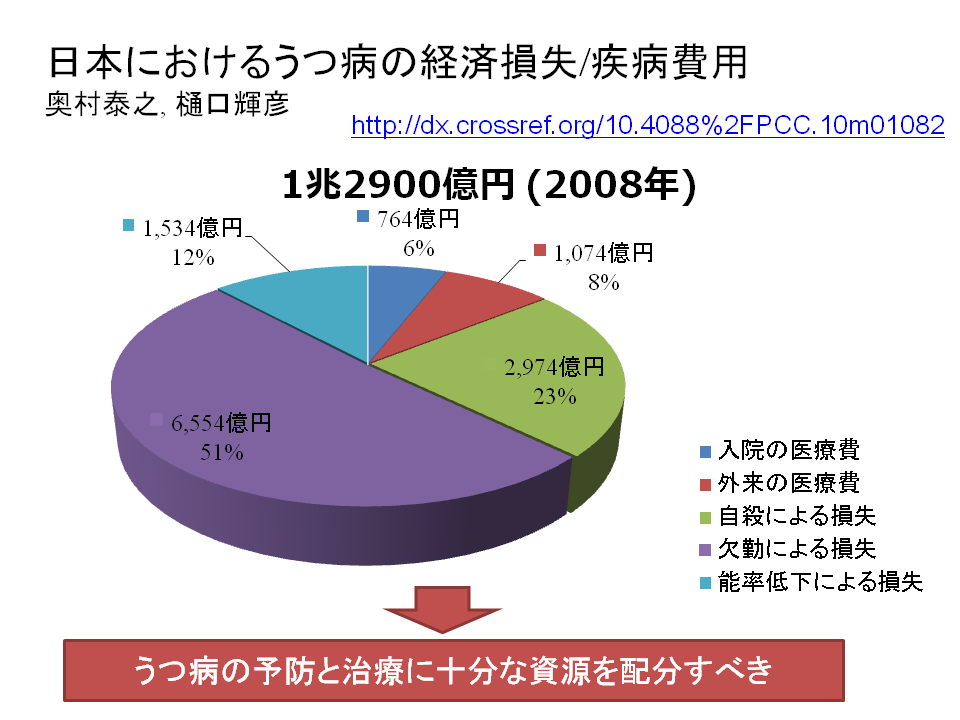 |
関連論文
- Okumura Y, Ito H: Out-of-pocket expenditure burdens in patients with cardiovascular conditions and psychological distress: a nationwide cross-sectional study. General Hospital Psychiatry 35(3): 233-8, 2013.
|
Cited by
- Sekizawa Y et al: Does the Three Good Things Exercise Really Make People More Positive and Less Depressed? A study in Japan. RIETI Discussion Paper Series 15-E-001, 2015.
- Endo M et al: Risk factors of recurrent sickness absence due to depression: a two-year cohort study among Japanese employees. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 88 (1): 75-83, 2015.
- Law YK et al: The chronic impact of work on suicides and under-utilization of psychiatric and psychosocial services. Journal of Affective Disorders 168: 254-261. 2014.
- OECD: Making mental health count the social and economic costs of neglecting mental health care. OECD Publishing. 2014.
- 佐藤寛: うつ病. 総合リハビリテーション 42(11): 1071-1075, 2014.
- Wada K et al: The Economic Impact of Loss of Performance Due to Absenteeism and Presenteeism Caused by Depressive Symptoms and Comorbid Health Conditions among Japanese Workers. Ind Health 51 (5): 482-489, 2013.
- Endo M et al: Recurrence of Sickness Absence due to Depression after Returning to Work at a Japanese IT Company. Ind Health 51 (2): 165-171, 2013.
- Xu et al: Depression in Asia: In Need of Greater Recognition. Journal of Asian Health.
- 北村文彦, 横山和仁: メンタルヘルス不調の早期支援のあり方. 産業医学レビュー 24: 13-31, 2011.
|
